
Position, y, as a function of time, t, along the x-axis. To represent a mass on a rubber band or spring and the graph on the right plots the Warning! I made the image myself and I am no Walt Disney animator. That shows how the displacement of a simple harmonic oscillator varies with time.
To identify these parameters in different examples of SHM. What you do need to know is the meaning of the symbols in the formula and be able We won't do too much with the formula but here it is: You remember sine and cosine functions from your trig classesĭon't you?]. Mass varies sinusoidally (whoa, big word!) as a function of time. What is the simple mathematical form of SHM motion? The displacement of the oscillating To get the spring back to its original shape. The more you stretch a spring the larger the force trying

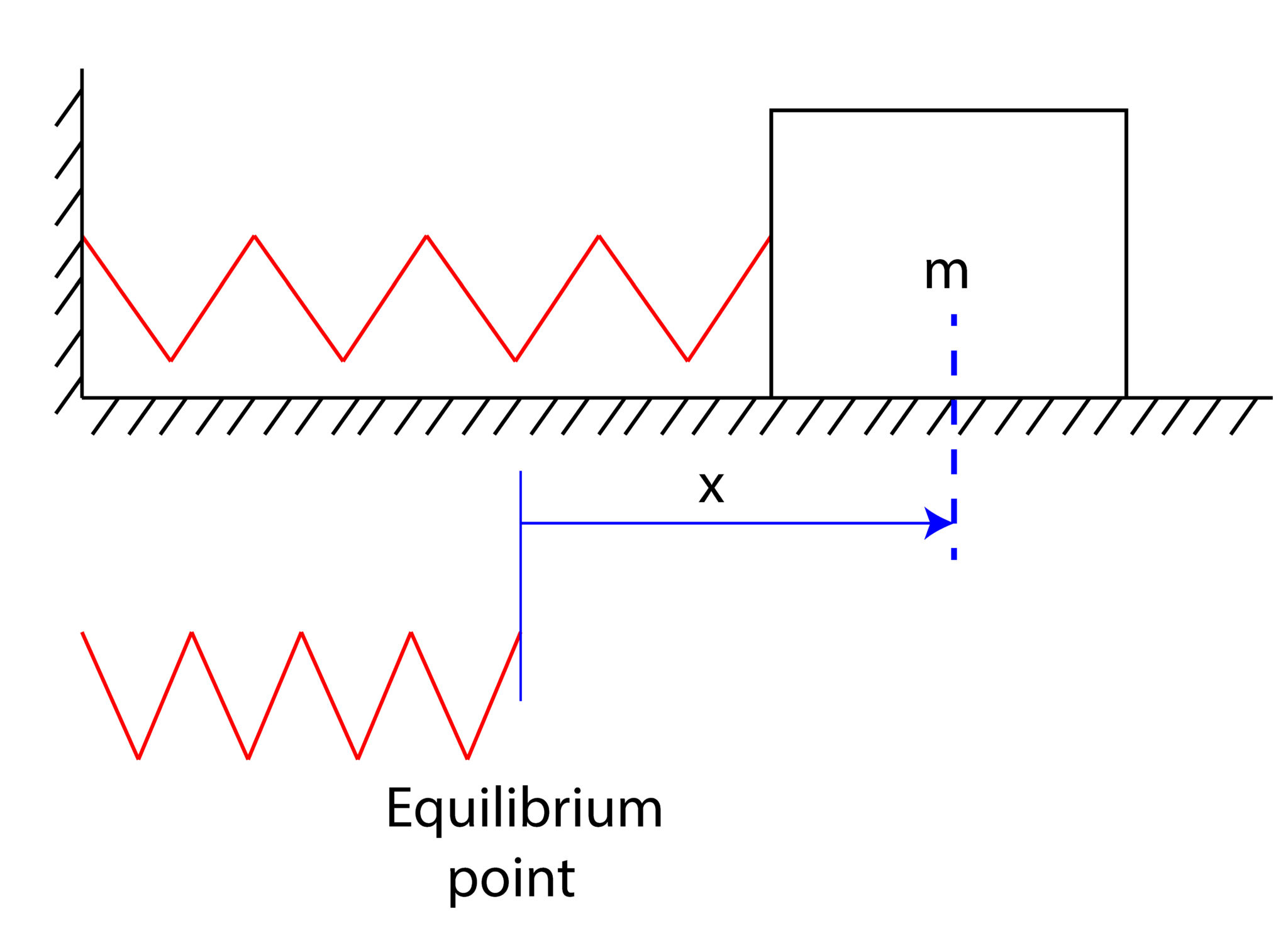
Gets progressively larger with diplacement from the equilibrium position. Mass is subject to a linear restoring force.

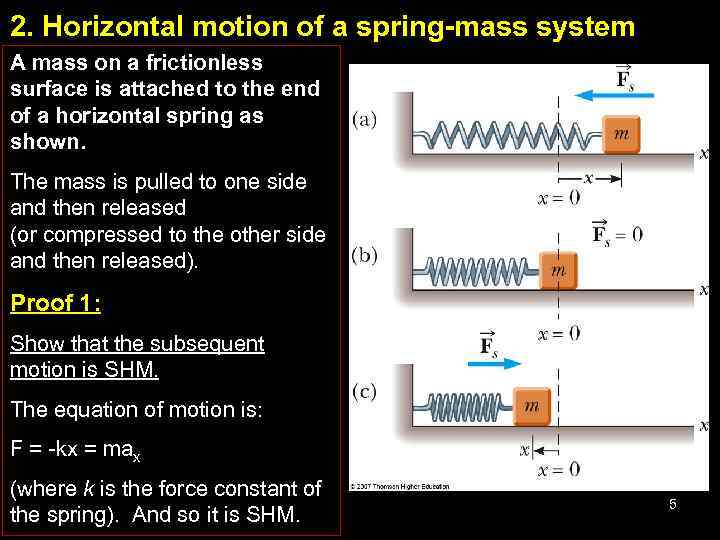
What is the physical principle? SHM occurs around an equilibrium position when a Of SHM have the same, very straightforward, mathematical description. Physicists like simple harmonic motion (let's begin abbreviating it SHM) because everyĮxample of SHM is based on the same underlying physical principle and all examples No shocks) that bounces down the road like a low-rider every time you hit a bump. Motion called simple harmonic motion. Simple harmonic motion occurs in a myriad ofĭifferent forms in the everyday world for example, a person bouncing on the end ofĪ diving board, a child in a swing, or your cousin's funky car (you know the one with However, to begin our analysis we look at the most basic type of periodic Motion that repeats in a regular pattern over and over again is called periodic motion.Īs we will come to appreciate, periodic motion is crucial to the production of musical


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
